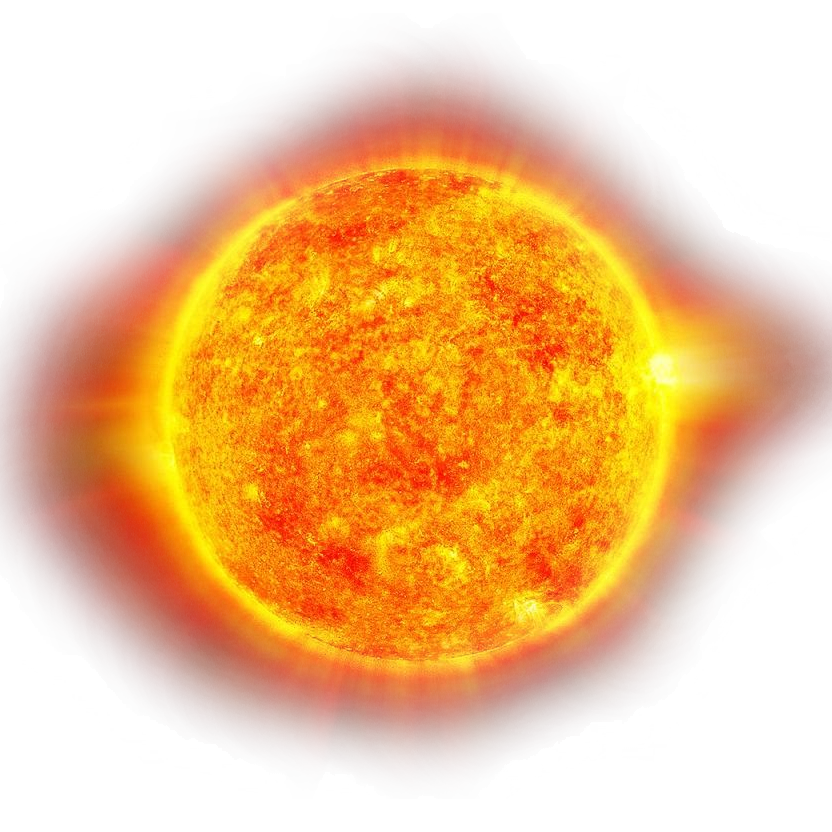
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect spherical ball of hot plasma. Its diameter is about 109 times Earth's, and it has a mass about 330,000 times Earth's. It's about 75% hydrogen and 25% helium.

Mercury
Mercury is the smallest and closest to the Sun of the eight planets in the Solar System, with an orbital period of about 88 Earth days. Seen from Earth, it appears to move around its orbit in about 116 days and it has no known natural satellites.
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun, orbiting it every 224.7 Earth days. It has no natural satellite. After the Moon, it is the brightest natural object in the night sky, reaching an apparent magnitude of −4.6, bright enough to cast shadows. Because Venus is an inferior planet from Earth, it never appears to venture far from the Sun.

Earth
Earth, is the third planet from the Sun, the densest planet in the Solar System, the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets, and the only astronomical object known to accommodate life. Earth gravitationally interacts with other objects in space, especially the Sun and the Moon. Earth's axis of rotation is tilted 23.4° away from the perpendicular of its orbital plane, producing seasonal variations on the planet's surface with a period of one tropical year (365.24 solar days). The Moon is Earth's only permanent natural satellite. Its gravitational interaction with Earth causes ocean tides, stabilizes the orientation of Earth's rotational axis, and gradually slows Earth's rotational rate.

Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second smallest planet in the Solar System, after Mercury. It is often referred to as the "Red Planet" because of the iron oxide prevalent on its surface. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere, having surface features reminiscent both of the impact craters of the Moon and the volcanoes, valleys, deserts, and polar ice caps of Earth. The rotational period and seasonal cycles are similar to those of Earth. Mars has two moons, Phobos and Deimos, which are small and irregularly shaped.

Asteroid Belt
The asteroid belt is located roughly between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. It is occupied by numerous irregularly shaped bodies called asteroids or minor planets. The asteroid belt is also termed the main asteroid belt or main belt to distinguish it from other asteroid populations in the Solar System. About half the mass of the belt is contained in the four largest asteroids: Ceres, Vesta, Pallas, and Hygiea. The total mass of the asteroid belt is approximately 4% that of the Moon.
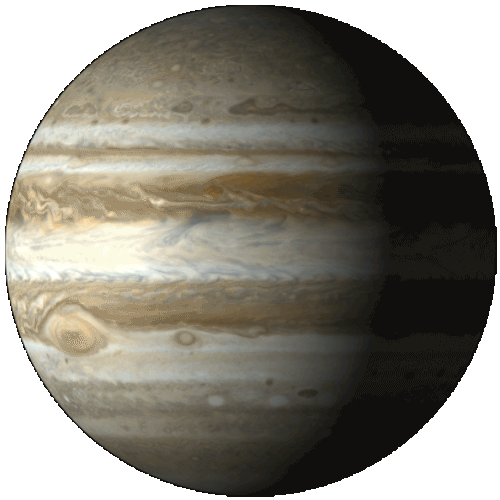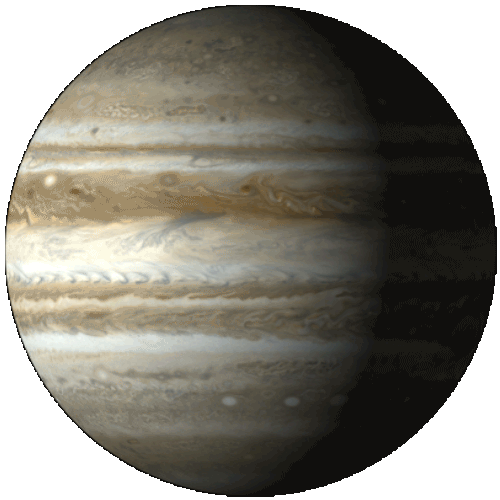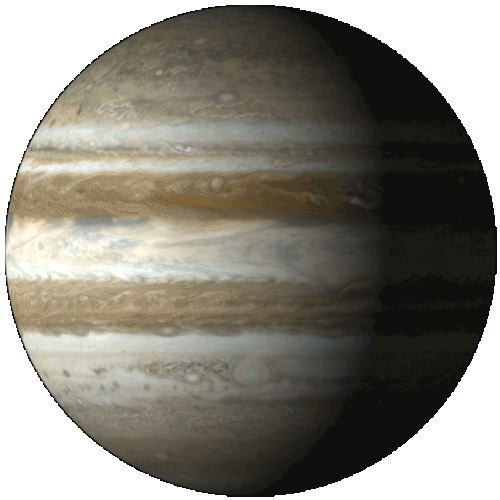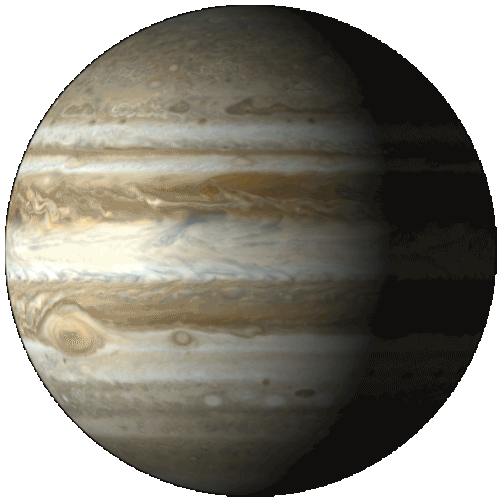
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet in the Solar System. It is a giant planet with a mass one-thousandth that of the Sun, but is two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined. Jupiter is a gas giant, along with Saturn (Uranus and Neptune are ice giants). Jupiter was known to astronomers of ancient times. When viewed from Earth, Jupiter can reach an apparent magnitude of −2.94, bright enough to cast shadows, and making it on average the third-brightest object in the night sky after the Moon and Venus.

Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius about nine times that of Earth. Although only one-eighth the average density of Earth, with its larger volume Saturn is just over 95 times more massive.
Saturn has a prominent ring system that consists of nine continuous main rings and three discontinuous arcs and that is composed mostly of ice particles with a smaller amount of rocky debris and dust.
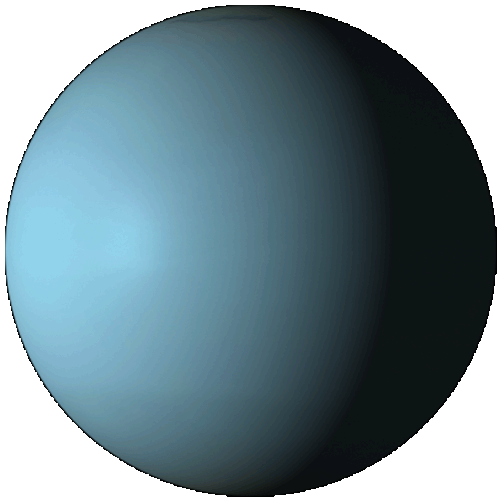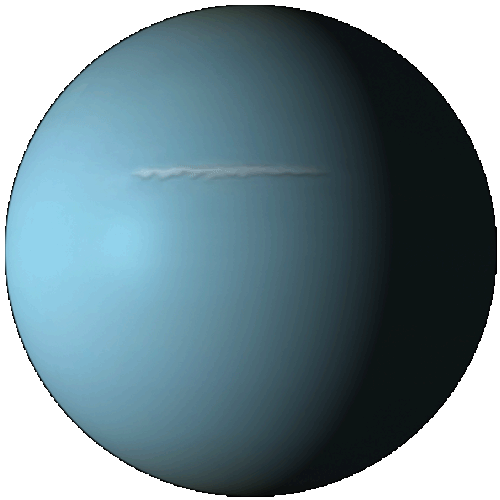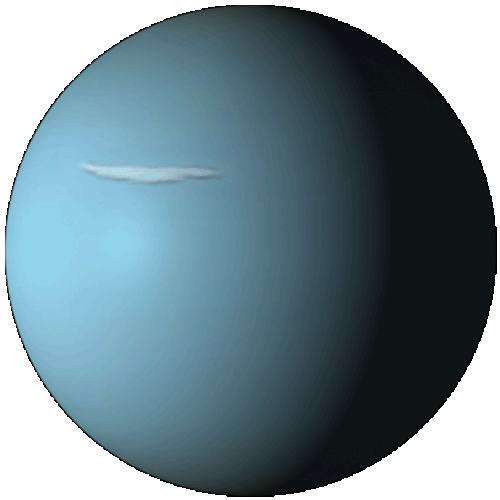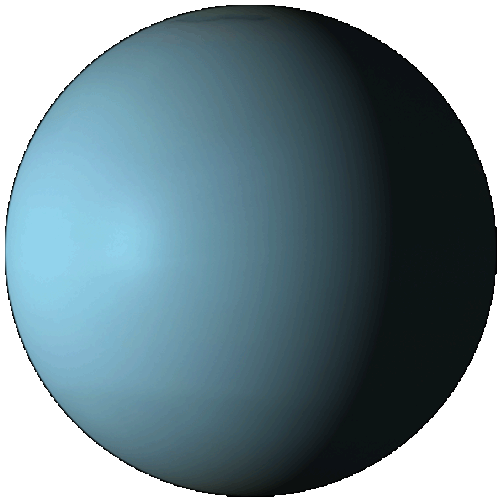
Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It has the third-largest planetary radius and fourth-largest planetary mass in the Solar System. Uranus is similar in composition to Neptune, and both have different bulk chemical composition from that of the larger gas giants Jupiter and Saturn. Uranus's atmosphere, although similar to Jupiter's and Saturn's, contains more "ices", such as water, ammonia, and methane. It is the coldest planetary atmosphere in the Solar System, with a minimum temperature of 49 K (−224.2 °C). The interior of Uranus is mainly composed of ices and rock.
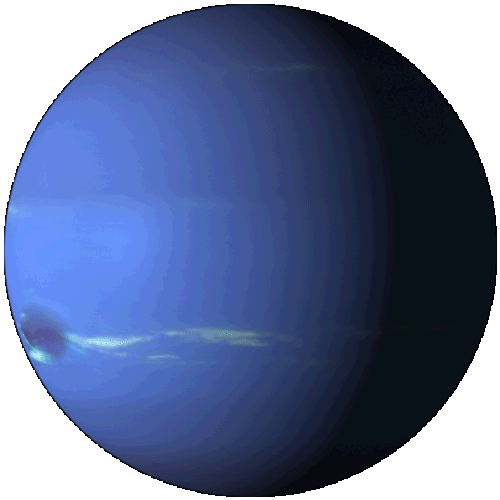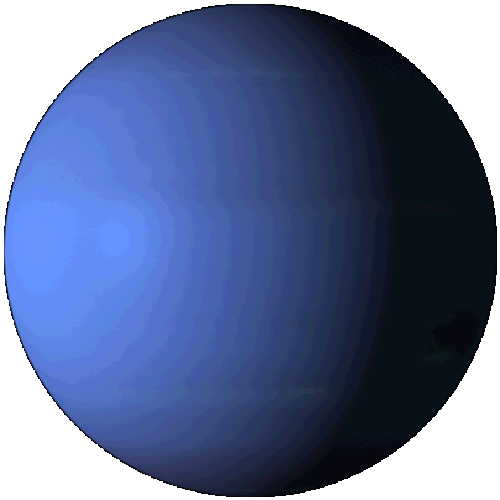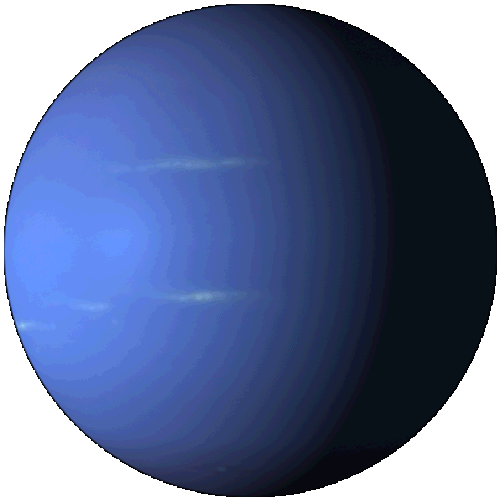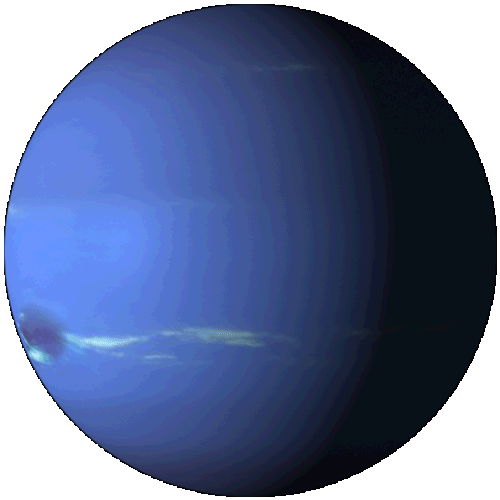
Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest planet from the Sun in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet by diameter and the third-largest by mass. Among the giant planets in the Solar System, Neptune is the most dense. Neptune is 17 times the mass of Earth and is slightly more massive than Uranus. Neptune orbits the Sun at an average distance of 30.1 astronomical units (4.50×109 km).



